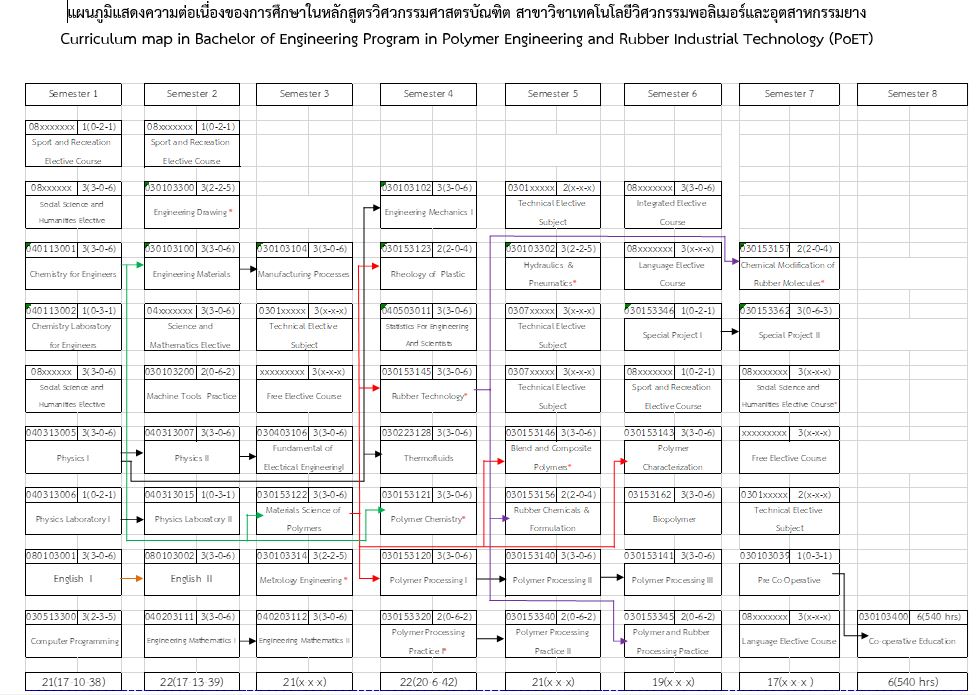
Polymer Engineering and Rubber Industrial Technology
Polymer and rubber materials play an important role in our daily lives and are widely used and applied in all industrial sectors such as electronics, automotive, and medical devices. Polymer Engineering and Rubber Industrial Technology is a cooperative education program combining intensive theories and practices to improve students’ knowledge, skills, and abilities, particularly in polymer and rubber materials. Basic polymer theories, processing, characterization, and machine are practiced in the classroom to serve the basic and advanced knowledge of polymer and rubber in this program. This is consistent with the country’s policy of manufacturing the polymer and rubber industrial sectors, widely used around the world. This cooperative program combines classroom learning with real-world work experience, as well as practices over a 4-month or 1-semester on-the-job training in the private or public sectors. Students are also taught research skills in polymer and rubber products, as well as how to solve problems in project subjects before going out to practice. Students learn how to think critically, analyze data, and conduct research that can be experience in the real world.
Program 4 years Credits 149 Credits
ELO 2 (S) be able to identify and solve complex problems in polymers engineering and rubber industrial technology using principles and analytical tools from mathematics, science, and engineering.
ELO 3 (S) be able to design technological processes in the polymer engineering and rubber industrial technology in accordance with job requirements and taking into account social, safety, health, and environmental requirements or professional practice standards.
ELO 4 (S) be able to analyze complex polymer engineering and rubber industrial technology problems, assuming an experimental design Data interpretation and information synthesis in order to reach rational and correct conclusions.
ELO 5 (S) be able to apply suitable and up-to-date information technology, techniques, methods, resources and equipment in engineering, polymer engineering and rubber industrial technology, taking into account the requirements and limitations of those tools and equipment in accordance with the correct principle.
ELO 6 (G) be able to work with people from various backgrounds, disciplines, and possess leadership.
ELO 7 (G) be able to communicate, present, have engineering drawing skills, and work in a team.
ELO 8 (G) be able demonstrate responsibility for the practice of the engineering profession. in the context of society, the environment, and sustainable development.
ELO 9 (G) be able to demonstrate morality, ethics, and engineering ethics.
ELO 10 (G) be able to apply knowledge of economics and management in the production process polymer engineering and rubber industrial technology considering the risks and situations of polymer engineering and rubber industrial technology in the country and the world economy.
ELO 11 (G) be able to apply knowledge for self-development in lifelong learning enhance one’s quality of life and live
– Students must be a graduate of senior high school (Mattayom 6) in Mathematics-Science and Technology or Art-Science and have completed at least 30 credits of Mathematics-Science and Technology subjects. (or)
– Student must have other qualifications according to the regulations of King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok regarding bachelor’s degree
| 1) Total Credits | 149 | Credits | |||||
| 1) General Education Subjects | 30 | Credits | |||||
|
a. Languages Subjects – Compulsory Subjects – Elective Subjects |
12 6 6 |
Credits Credits Credits |
|||||
| b. Integration Subjects | 3 | Credits | |||||
| c. Social and Humanity Subjects | 9 | Credits | |||||
| d. Science and Mathematics Subjects | 3 | Credits | |||||
| e. Sports and Recreation Subjects | 3 | Credits | |||||
| 2) Specialization Subjects | 113 | Credits | |||||
|
1. Core Subjects – Mathematics and Science Fundamentals Subjects |
48 21 27 |
Credits Credits Credits |
|||||
|
2. Professional Subjects – Compulsory Subjects – Technical Elective subjects |
58 45 13 |
Credits Credits Credits |
|||||
| 3. Co-operative Subjects | 7 |
Credits
|
|||||
| 3) Fee Elective Subjects | 6 | Credits | |||||
Semester 1: June – September
Semester 2: November – February
Summer semester: April – May
Potential Careers after Graduation:
- Polymer materials and production engineer
- Rubber engineer
- Process engineer
- Research and development engineer in government agencies and private companies
- Quality control engineer
- Entrepreneur/Business owner
- Educational personnel
- Other occupations related to polymer and rubber processing.
Contact Details:
Division of Polymer Engineering and Rubber Industrial Technology
2nd Floor Building 69
College of Industrial Technology
King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok
1518 Pracharat 1 Rd. Wongsawang Bangsue Bangkok 10800
![]() +66 2 555-2000 ext. 6408
+66 2 555-2000 ext. 6408
![]() Asst. Prof. Dr. Pornsri Sapsrithong (pornsri.s@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)
Asst. Prof. Dr. Pornsri Sapsrithong (pornsri.s@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)
Asst. Prof. Dr. Apaipan Rattanapan (apaipan.r@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)
Asst. Prof. Dr. Surakit Tuampoemsab (surakit.t@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)
Asst. Prof. Dr. Thritima Sritapunya (thritima.s@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)
Asst. Prof. Dr. Nathapong Sukhawipat (nathapong.s@cit.kmutnb.ac.th)

